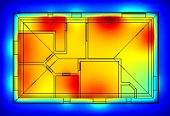
Regular inspection is focused on boilers and smoke flue, its accessories, security and regulation. The article presents the second example of inspection of an old thermal system with modern atmospheric gas boiler in a house with new windows and thermoinsulation of the facade.
Archiv článků od 12.12.2011 do 5.3.2012
Regular inspection is focused on boilers and smoke flue, its accessories, security and regulation. The article presents an example of inspection of the thermal system with older atmospheric gas boiler in a house without insulation. Technical details of the revision are completed with final report as a result of the inspection .
The use of GE depends on the predisposition source, namely geothermal boreholes. The use itself is different when using the heat for heating, hot water, heating greenhouses and plastic greenhouses (agricultural), recreation facilities, but also for various technologies. The inclusion of monitoring and control system for an open geothermal energy system is achieved by taking friendly geothermal water and substantially increases the life of the whole work.
The author in his article deals with intermittent heating of buildings, specifically optimizing the operation of the heating system so that the change in the heating mode - in compliance with the required quality of the indoor environment during the heating breaks - achieved economic savings due to reduced output of the heating system design.
Supply of gas or electricity is so important that many customers do not want to risk a possible interruption when changing suppliers. New legislative rules defined in an amendment to the Energy Act No. 458/2000 Coll. (as amended by Act No. 211/2011 Coll.) but fill existing gaps in legislation and establish a procedure for changing supplier.
The article describes the methodology of experimental verifying of the performance of heat pump in real conditions. Namely the air-water type of heat pump was evaluated. Heat pump has been observed in extreme climatic conditions and the resulting measured and calculated parameters were compared with the parameters specified by its manufacturer.
The aim of the authors is to evaluate the economic effectiveness of choosing of the heating system for family passive houses and to compare it with the same systems used in common buildings. Methodology of the comparison consist in real market offers and price lists in price level of first half-year 2011. The work is based on the case study of simulated passive house. The result encompasses confrontation of the overall costs of energy supply for family house for 15 years. At the end of the article the overall benefits of passive houses building and management are discussed.
Regular inspection is focused to the boiler, smoke flue and accessories condition, its security and regulation. In addition to the technical condition and maintenance, the documentation, operating instructions, manuals and other documents are under inspection. It quantifies the overall boiler efficiency of measurement results, sets reference respectively minimum boiler efficiency and suggests possible actions.
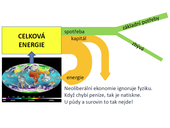
Oil is the energy source No. 1, and the world is in a period of peak oil. Serious paralysis of economy after peak oil is almost certain, because economic growth demanded increasing consumption of fossil fuels from the beginning of the industrial revolution.
The Czech Republic can ensure its energy security only in integrating with Europe, and especially the connection to Europe's energy (especially electricity and gas) and transport networks and participation in the transformation of post-fossil energy and transport system.
Long-term air quality data collected in areas affected by pollution from large industrial sources, reported during the heating season, the remarkable changes that indicate a significant proportion of small sources in impaired air quality. Residents and their boiler is considerable work involved in air pollution.
Chimneys should be so high above the immediate surroundings, so as not to affect the environment or not to affect the area by polluted flue gases. During the operation it should be excluded interference of surrounding objects on the function of chimney. The article summarizes the conditions for the design of the chimney outlet on sloped and flat roofs.
The growth of a company cannot be planned as has been shown by the economic recession. But if this is taken into account when constructing its registered office, it is not necessary to move elsewhere. The owner of a Litoměřice company believed in its development and after ten years in co-operation with the architect Zuzana Hamanová he enlarged the administrative building and the production hall with other premises including a research and development centre.
In 2010 it was delivered to the domestic market, over 80 thousand small combustion plants for solid fuels. Of these, 24 000 stove and fireplace inserts, stoves 50 000, less than 5000 kitchen ranges and over 1000 spa stoves. Around 50% of these devices are imported. Hot-water heat exchanger is fitted with 15-20% of sold heaters.
Making sense of saving heat is difficult even for experts, let alone for the Laity. When we don't heat an object, is it to save 100 % or nothing? Making sense of savings means working with the measured consumption, the transfer values for the normal year and saving heat show in the difference between the values of normal years. Check with us to turn out such assessments.
zpět na aktuální články